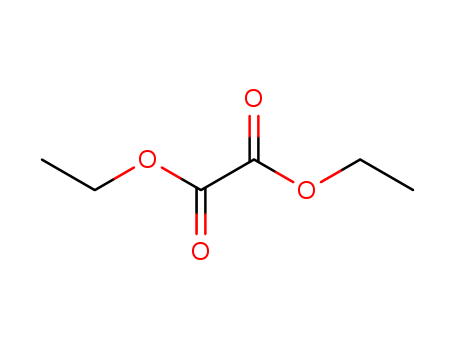
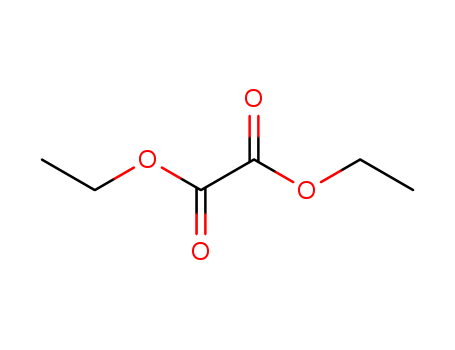
Cyanide selective chemodosimeter in aqueous medium, on test strips and its application in real sample analysis
Ghosh, Tamal,Raina, Ashish,Singh, Yadvendra,Yadav, Komal Kumar
, (2020)
Abstract: In this paper, synthesis, char...
Highly active Pd-Fe/α-Al2O3 catalyst with the bayberry tannin as chelating promoter for CO oxidative coupling to diethyl oxalate
Xing, Wei-Chao,An, Ji-Min,Lv, Jing,Irshad, Faisal,Zhao, Yu-Jun,Wang, Sheng-Ping,Ma, Xin-Bin
, p. 796 - 800 (2021)
A novel Pd-Fe/α-Al2O3 catalyst was synth...
-
Fenton,Steinwand
, p. 701 (1974)
-
-
Jewel,Butts
, p. 3560 (1931)
-
A nanostructured CeO2 promoted Pd/α-alumina diethyl oxalate catalyst with high activity and stability
Jin, Erlei,He, Leilei,Zhang, Yulong,Richard, Anthony R.,Fan, Maohong
, p. 48901 - 48904 (2014)
A Pd/α-Al2O3 nanocatalyst was synthesize...
One-pot production of diethyl maleate via catalytic conversion of raw lignocellulosic biomass
Cai, Zhenping,Chen, Rujia,Jiang, Lilong,Li, Fukun,Li, Xuehui,Long, Jinxing,Zhang, Hao
supporting information, p. 10116 - 10122 (2021/12/24)
The conversion of lignocellulose into a ...
Method for continuously producing diethyl oxalate
-
Paragraph 0077-0091, (2021/06/21)
The invention provides a method for cont...
PROCESS FOR THE SYNTHESIS OF ETHYLENE GLYCOL
-
Page/Page column 49-51, (2021/10/11)
The invention relates to a process for t...
中文
English
Japanese
Russian
Korean
गोंगेन हें नांव
Deutsch
Corsu
Guarani
Hausa
Cymraeg
Nederlands
Aymara
Français
Kreyòl ayisyen
čeština
ʻŌlelo Hawaiʻi
डोग्रिड ने दी
ภาษาไทย
հայերեն
فارسی
Hmoob
ދިވެހި
भोजपुरी
繁體中文
Türkçe
हिंदी
беларускі
български
tur
Gaeilge
ગુજરાતી
Magyar
Eesti keel
بالعربية
বাংলা
Azərbaycan
Português
Suid-Afrikaanse Dutch taal
کوردی-سۆرانی
Ελληνικά
español
Frysk
dansk
አማርኛ
Bamanankan
euskara
Italiano
Tiếng Việt
অসমীয়া
català
Suomalainen
Eʋegbe
Hrvatski
Cebuano
Gàidhlig na h-Alba
bosanski
galego