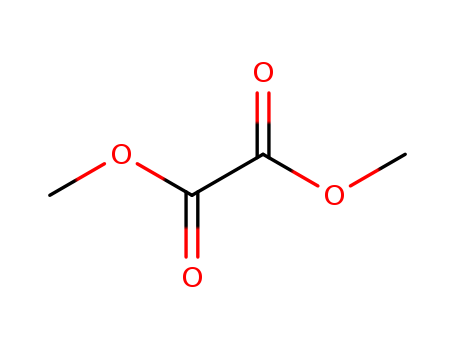
Cyclization of Dimethyl Oxalate upon Electron Impact
Liehr, J. G.,Larka, E. A.,Beynon, J. H.
, p. 34 - 36 (1981)
Isotope labelling experiments and also c...
Mechanistic study of the oxidative carbonylation of methanol catalyzed by palladium diphosphane complexes with nitrobenzene as oxidant
Mooibroek, Tiddo J.,Bouwman, Elisabeth,Drent, Eite
, p. 1403 - 1412 (2012)
The reactivity of Pd complexes having bi...
Catalytic Synthesis of Oxalate Esters
Current, Steven P.
, p. 1779 - 1780 (1983)
A new catalyst system, palladium(II) ace...
Lewis acid sites in MOFs supports promoting the catalytic activity and selectivity for CO esterification to dimethyl carbonate
Guo, Guo-Cong,Jing, Kai-Qiang,Tan, Hong-Zi,Wang, Zhi-Qiao,Xu, Yu-Ping,Xu, Zhong-Ning
, p. 1699 - 1707 (2020)
CO esterification to dimethyl carbonate ...
Catalyst design criteria and fundamental limitations in the electrochemical synthesis of dimethyl carbonate
?ari?, Manuel,Davies, Bethan Jane Venceslau,Schj?dt, Niels Christian,Dahl, S?ren,Moses, Poul Georg,Escudero-Escribano, María,Arenz, Matthias,Rossmeisl, Jan
, p. 6200 - 6209 (2019)
Dimethyl carbonate is an environmentally...
A kinetic study of the solvolyses of methyl and ethyl chloroglyoxalates
Kevill, Dennis N.,Park, Byoung-Chun,Kyong, Jin Burm
, p. 9032 - 9035 (2005)
Solvolyses of methyl and ethyl chlorogly...
Remarkable Decrease in Overpotential of Oxalate Formation in Electrochemical CO2 Reduction by a Metal-Sulfide Cluster
Kushi, Yoshinori,Nagao, Hirotaka,Nishioka, Takanori,Isobe, Kiyoshi,Tanaka, Koji
, p. 1223 - 1224 (1995)
Triangular metal-sulfide cluster, 3(μ3-S...
New aspects of the synthesis of dimethyl carbonate via carbonylation of methyl alcohol promoted by methoxycarbonyl complexes of palladium(II)
Cavinato, G.,Toniolo, L.
, p. C65 - C66 (1993)
suspended in MeOH reacts with carbon mo...
Active Pd(II) complexes: Enhancing catalytic activity by ligand effect for carbonylation of methyl nitrite to dimethyl carbonate
Tan, Hong-Zi,Wang, Zhi-Qiao,Xu, Zhong-Ning,Sun, Jing,Chen, Zhe-Ning,Chen, Qing-Song,Chen, Yumin,Guo, Guo-Cong
, p. 3785 - 3790 (2017)
Palladium (Pd)-based catalysts have been...
MgO: An excellent catalyst support for CO oxidative coupling to dimethyl oxalate
Peng, Si-Yan,Xu, Zhong-Ning,Chen, Qing-Song,Wang, Zhi-Qiao,Chen, Yumin,Lv, Dong-Mei,Lu, Gang,Guo, Guo-Cong
, p. 1925 - 1930 (2014)
Pd/MgO catalysts are found, for the firs...
Low-temperature synthesis of α-alumina nanosheets on microfibrous-structured Al-fibers for Pd-catalyzed CO oxidative coupling to dimethyl oxalate
Wang, Chunzheng,Xu, Weisong,Qin, Zhengxing,Liu, Xinmei,Mintova, Svetlana
, p. 158 - 166 (2020)
We reported the low-temperature synthesi...
A Stable Lithium–Oxygen Battery Electrolyte Based on Fully Methylated Cyclic Ether
Huang, Zhimei,Zeng, Haipeng,Xie, Meilan,Lin, Xing,Huang, Zhaoming,Shen, Yue,Huang, Yunhui
, p. 2345 - 2349 (2019)
Ether-based electrolytes are commonly us...
Selectivity Control of Carbonylation of Methanol to Dimethyl Oxalate and Dimethyl Carbonate over Gold Anode by Electrochemical Potential
Funakawa, Akiyasu,Yamanaka, Ichiro,Takenaka, Sakae,Otsuka, Kiyoshi
, p. 5346 - 5347 (2004)
New and unique electrocatalysis of gold ...
Palladium catalyzed oxidative carbonylation of alcohols: Effects of diphosphine ligands
Amadio, Emanuele,Freixa, Zoraida,Van Leeuwen, Piet W. N. M.,Toniolo, Luigi
, p. 2856 - 2864 (2015)
The catalytic activity of a series of pa...
-
Friess,Miller
, p. 2611 (1950)
-
An ultra-low Pd loading nanocatalyst with high activity and stability for CO oxidative coupling to dimethyl oxalate
Peng, Si-Yan,Xu, Zhong-Ning,Chen, Qing-Song,Chen, Yu-Min,Sun, Jing,Wang, Zhi-Qiao,Wang, Ming-Sheng,Guo, Guo-Cong
, p. 5718 - 5720 (2013)
A Pd/α-Al2O3 nanocatalyst with ultra-low...
New series of γ-pyrone based podands: Synthesis, characterization and study of their application in acetate salts cation trapping for nucleophilic substitution reactions
Teimuri-Mofrad, Reza,Aghaiepour, Alireza,Rahimpour, Keshvar
, p. 121 - 132 (2019)
Dialkyl 4-oxo-4H-pyran-2,6-dicarboxylate...
Pd/Mg(OH)2 Heterogeneous Nanocatalysts Synthesized by a Facile One-Pot Hydrothermal Method for CO Direct Esterification to Dimethyl Oxalate
Lin, Xiao-Qi,Wang, Zhi-Qiao,Xu, Zhong-Ning,Guo, Guo-Cong
, p. 3213 - 3219 (2021)
Pd-based heterogeneous nanocatalysts hav...
Dynamic Kinetic Cross-Electrophile Arylation of Benzyl Alcohols by Nickel Catalysis
Guo, Peng,Wang, Ke,Jin, Wen-Jie,Xie, Hao,Qi, Liangliang,Liu, Xue-Yuan,Shu, Xing-Zhong
supporting information, p. 513 - 523 (2021/01/12)
Catalytic transformation of alcohols via...
Ultralow-Molecular-Weight Stimuli-Responsive and Multifunctional Supramolecular Gels Based on Monomers and Trimers of Hydrazides
Wu, Dehua,Song, Jintong,Qu, Lang,Zhou, Weilan,Wang, Lei,Zhou, Xiangge,Xiang, Haifeng
supporting information, p. 3370 - 3378 (2020/10/02)
The simpler, the better. A series of sim...
中文
English
Japanese
Russian
Korean
गोंगेन हें नांव
Deutsch
Corsu
Guarani
Hausa
Cymraeg
Nederlands
Aymara
Français
Kreyòl ayisyen
čeština
ʻŌlelo Hawaiʻi
डोग्रिड ने दी
ภาษาไทย
հայերեն
فارسی
Hmoob
ދިވެހި
भोजपुरी
繁體中文
Türkçe
हिंदी
беларускі
български
tur
Gaeilge
ગુજરાતી
Magyar
Eesti keel
بالعربية
বাংলা
Azərbaycan
Português
Suid-Afrikaanse Dutch taal
کوردی-سۆرانی
Ελληνικά
español
Frysk
dansk
አማርኛ
Bamanankan
euskara
Italiano
Tiếng Việt
অসমীয়া
català
Suomalainen
Eʋegbe
Hrvatski
Cebuano
Gàidhlig na h-Alba
bosanski
galego